
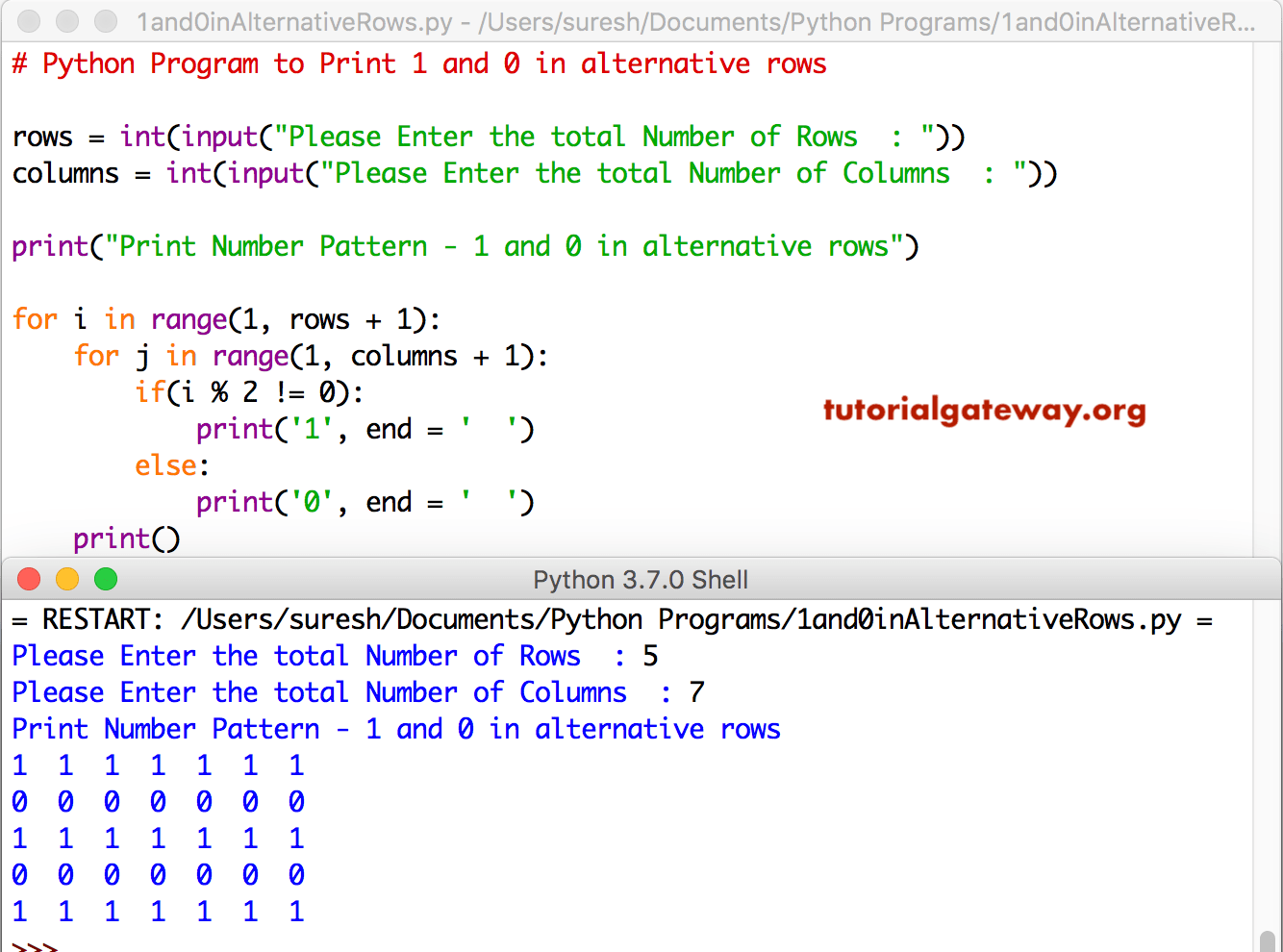
Python for loop executes a block of code or statement repeatedly for a fixed number of times. See: Python for loop and range() exercise for loop with range() If a step=0, Python will raise a ValueError exception.
Python will raise a ValueError exception if you set the step to 0.Here you can specify a different increment by adding a step parameter. When you pass all three arguments to the range(), it will return a sequence of numbers, starting from the start number, increments by step number, and stops before a stop number. The range will return an empty sequence if you set the stop value lesser than the start.When you pass two arguments to the range(), it will generate integers starting from the start number to stop -1. If you want to start the range at 1 use range(1, 10).If you set the stop as a 0 or some negative value, then the range will return an empty sequence.Here, start = 0 and step = 1 as a default value.When you pass only one argument to the range(), it will generate a sequence of integers starting from 0 to stop -1.

Now, let’s see all the possible scenarios. It is nothing but a difference between each number in the result. Each next number in the sequence is generated by adding the step value to a preceding number. The range() never includes the stop number in its result
#FOR I IN RANGE PYTHON HOW TO#
How to use range() function in Python Syntaxīelow is the syntax of the range() function. Concatenating the result of two range().Iterate a list using range() and for loop.Points to remember about range() function.trying to do it manually with a negative increment. If you want to loop over the index numbers of a string or list backwards, it's easier to use reversed() above, vs. > list(range(4, 5, -2)) # beyond the stop is omitted > list(range(5, 5, -2)) # equal to stop is omitted As always, numbers reaching or beyond the stop are omitted, but now step is decreasing. If the step is negative, the range decreases from start down to stop. As before, the stop number itself is always omitted. Once the number is equal or goes beyond the stop, the range ends. The difference is the "step" amount between numbers is now custom. The 3 parameter form begins with start number, up to but no including the stop number as usual. Range(start, stop, step) - 3 Parameter Form Mnemonic: the "stop" number is strong, so as soon as the numbers hit or exceed the stop the range is done (even if the start number initiates things in that position). > list(range(5, 5)) # start >= stop, no numbers Range with 2 parameters specifies a start number other than 0, but is otherwise like the 1 parameter form above, going up to but not including the stop number. This works nicely with range() to go over the regular numbers in reverse order: The reversed() function takes in a linear collection and returns a reversed form of it. Probably the second most common problem is to go through the standard index numbers, but in reverse order. What is range(0)? Well range(n) returns n numbers, so this case returns no numbers at all - like the empty list. This use of list() is only for printing, not needed to use range() in a loop. For cosmetic reasons in the examples below, the call of the range() function is inside a list() so the numbers will print out. This is perfect for generating the index numbers into, for example, a string.īelow are some more examples calling range().
#FOR I IN RANGE PYTHON SERIES#
Or put another way, range(n) returns a series of n numbers, starting with 0`. The most common form is range(n), for integer n, which returns a numeric series starting with 0 and extending up to but not including n, e.g. The range() function can be called in a few different ways. This is very useful, since the numbers can be used to index into collections such as string. The python range() function creates a collection of numbers on the fly, like


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
